Decorative Materials
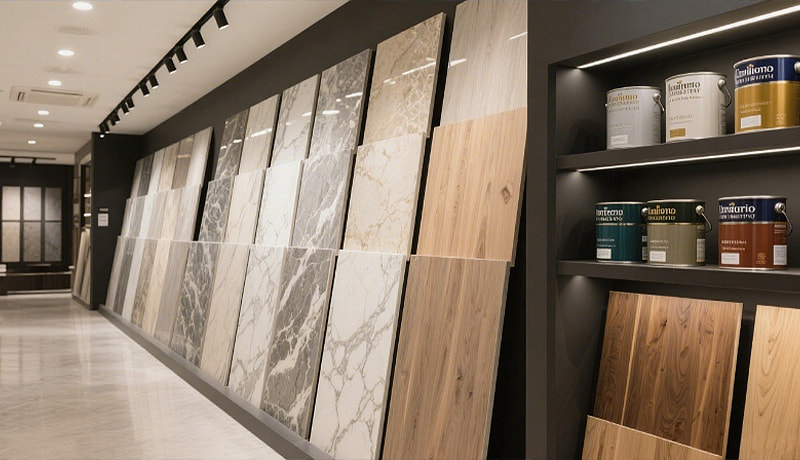
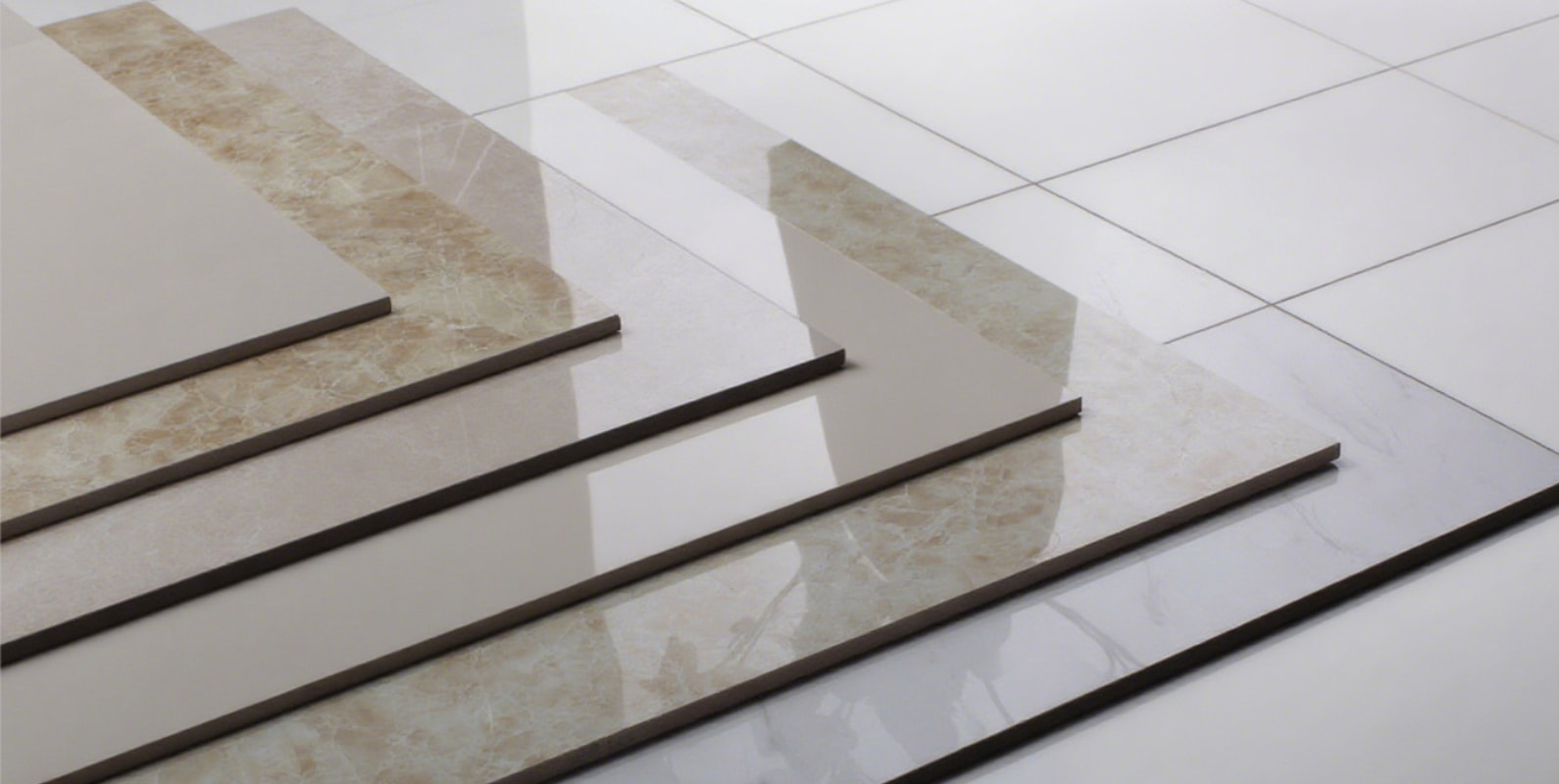
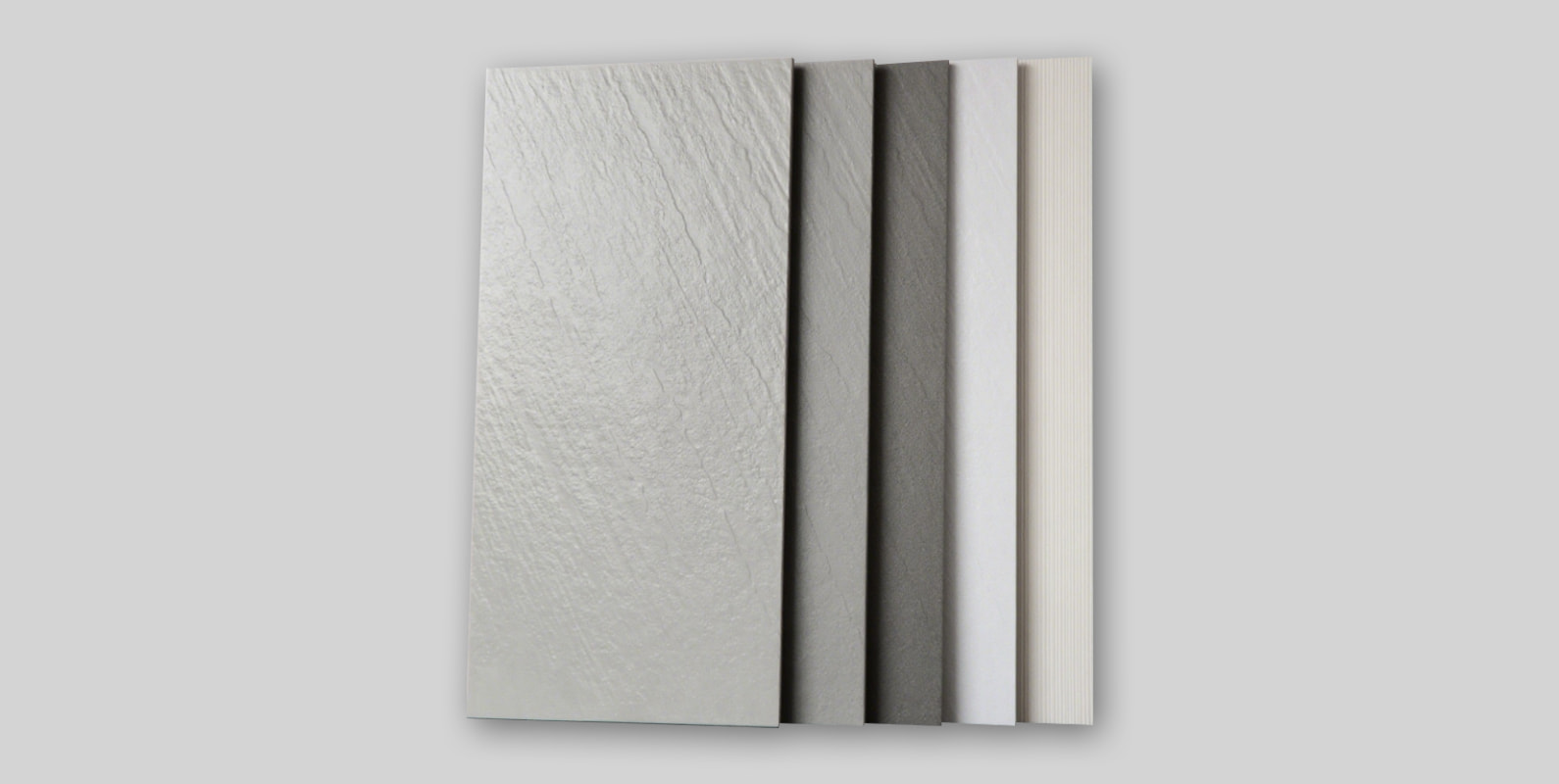
As a fundamental element of architectural finishes, decorative building materials encompass a wide range of categories—from tiles and wallpapers that enhance spatial aesthetics to doors, ceiling materials, and moldings that define interior style, as well as coatings and trim details that elevate overall texture and quality. These materials offer a rich variety of textures, colors, and forms to meet the visual demands of both interior and exterior spaces, helping create distinctive atmospheres and design identities. Beyond appearance, they also emphasize durability, environmental friendliness, and ease of maintenance. In architectural decoration projects, decorative materials play a vital role in shaping comfortable, beautiful, and high-quality living and commercial environments—bridging the transition from structural construction to refined, aesthetic living spaces.


 中文简体
中文简体 English
English